A Comprehensive Guide to Private 5G Networks

You must have noticed that the capabilities of private 5G networks are widely discussed recently.
According to the GSA (Global mobile Suppliers Association), 5G remains on track to become the fastest adopted mobile technology ever.
Mid-September figures indicate that 397 operators in 129 markets are at various stages of 5G deployment, including license acquisition, planning, testing, network deployment, and actual launches. In terms of live networks, 124 operators have deployed 3GPP compliant technology of which 101 already offer one or more 3GPP-compliant 5G services across 44 markets.
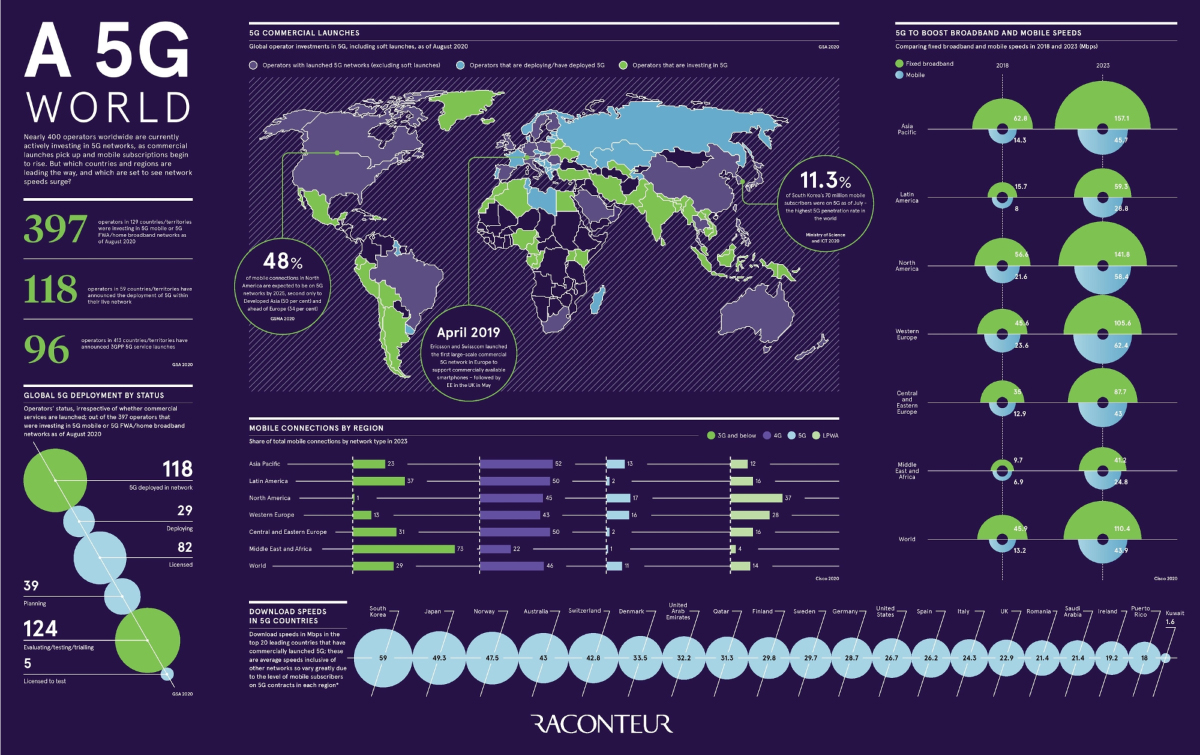
Image source: Visual Capitalist
However, there is a wide global variation in terms of consumer sentiment towards 5G both in terms of intent to upgrade and willingness to pay more for it. In fact, only a third of consumers acknowledge the potential for 5G to deliver innovative new services with a majority just expecting faster mobile data connections.
The impact of 5G on the business world, on the other hand, is expected to be more immediate and significant. According to a GSMA Intelligence report, 5G is expected to be the first generational mobile technology to have a bigger impact on enterprises than consumers. The report even predicts a rapid proliferation of private enterprise networks over the next 5 years with telcos and cloud companies battling for the honors.
The focus of this article, therefore, will be on private 5G networks and their ability to incubate innovative B2B applications and services.
What are Private 5G Networks?
Private 5G networks refer to physical or virtual cellular systems deployed for private use by companies, governments, and other institutions.
According to the 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project), these Non-Public Networks (NPNs) can be deployed either as a stand-alone network operated independently without relying on network functions provided by a PLMN or as a public network-integrated NPN deployed with the support of a PLMN.
Even though Wi-Fi and 4G are already used widely in industrial applications, they were never designed specifically for business applications and have to be adapted to the specific needs of these environments.
In comparison, certain key specifications of 5G networks, such as ultra-low latency, high network availability, high device density capabilities, and large volume data aggregation, dovetail perfectly with the emergent needs of Industry 4.0.
Why Private 5G Networks though?
A Deloitte paper on the topic offers some concise insights into the value of investing in private 5G networks.
One of the advantages of private 5G networks is that they can be configured not only to specific enterprise needs but also to the requirements of specific venues or locations. Companies can accelerate the identification and resolution of network-related by deploying dedicated teams.
And finally, companies have more control over private than public networks which gives them more control over strategic issues like data access, residency and sovereignty, service levels, and security.
Key Requirements of Private 5G Networks
Networking and telecommunications giant Ericsson defines 5 key requirements for private 5G networks.
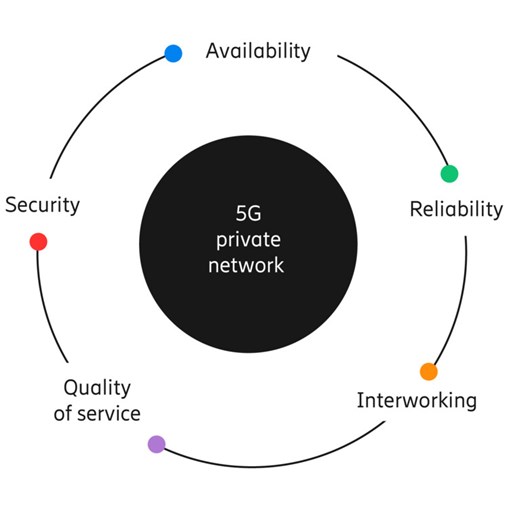
Image source: Ericsson
1. Private 5G networks must guarantee maximum availability through robust solutions and redundancies that reduce downtime to zero and afford more control over system maintenance.
2. Private 5G networks must provide adequate coverage, capacity, and handover functionality to increase reliability in data transmissions in terms of volume, duration, and the probability of success.
3. Private 5G networks must be capable of integrating and working with public 5G networks in order to ensure service continuity for mission-critical applications that may need to hop networks.
4. Private 5G networks should give enterprise teams more control over key Quality of Service metrics such as throughput, latency, jitter, packet drop rate, etc. and allow them to tailor system performance and resource consumption to specific needs within the network.
5. Private 5G networks must enable end-to-end security for data, infrastructure, and personnel by complying with the three main security principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
If the business-specific next-generation capabilities of 5G networks transcend the limitations of existing 4G technologies, then private 5G networks give companies complete control and flexibility in configuration, performance, upgradation, evolution, and security of their connected operations.
This new technology is expected to transform multiple industries such as manufacturing, transportation, healthcare, public infrastructure, etc.
And businesses are already experimenting with this new technology. One recent study from ABI Research tracked multiple enterprise initiatives across 15 countries to create private 5G networks either by acquiring spectrum directly from regulators or by leveraging the spectrum assets of MNOs.
Deloitte predicts that about a third of all spends in the private 5G market over the next five years will come from infrastructure operations like ports, airports, and similar logistics hubs.
Another manufacturing-focused study from Nokia and ABI research found that 84% of decision-makers in the sector were planning to deploy their own local private wireless network. And finally, there is a view that the ongoing pandemic could accelerate private 5G adoption.
Use Cases for Private 5G Networks
A study commissioned by Ericsson values the global addressable market for 5G-enabled B2B opportunities across 10 industries at $700 billion by 2030.
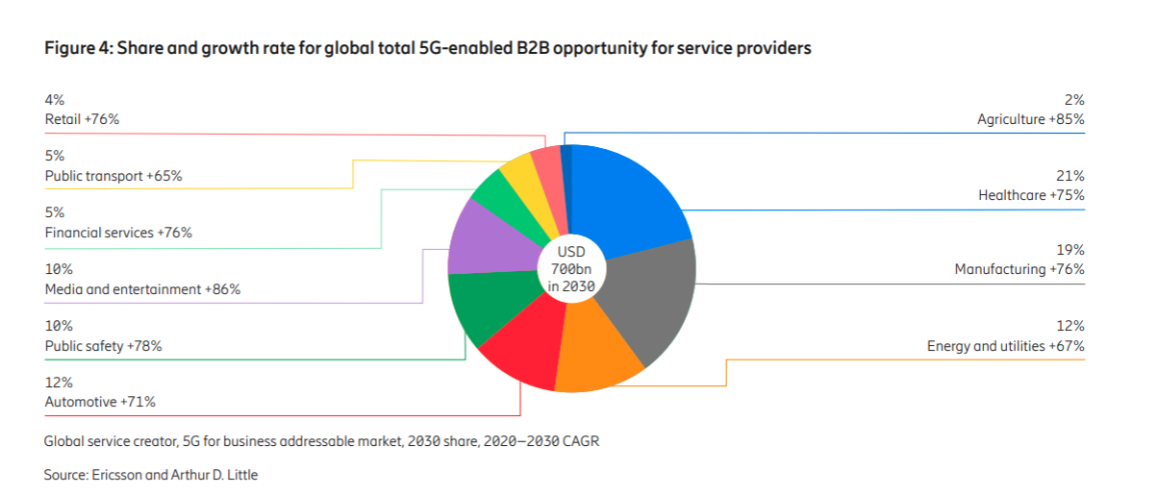
Image source: Ericsson
The study, which also analysed a range of 5G application scenarios from each of these industries as well as 9 use case clusters, identified 200 distinct use cases that were either “significantly enhanced” or “made at all possible to realize” by introducing 5G 3GPP technology. Use cases fulfilled by non-3GPP technologies did not make the cut.
Clearly, 5G-enabled technologies have a rather broad scope not only in terms of the industries they are relevant to but also in terms of the range of application possible within each sector. With that in mind, here’s a brief overview of some of the possible application scenarios from some of these sectors.
Public Transportation - Airports
The race to deploy private 5G in airports seems to have begun in earnest. This year, there has been a slew of announcements regarding private network deployments. Ericsson announced that it will deploy a private 4/5G mobile network covering Paris-Charles de Gaulle, Paris-Orly, and Paris-Le Bourget airports and serving a professional ecosystem of more than 120,000 people across about 1,000 companies.
Finland’s Helsinki Airport, partnered with Swedish telecommunications company Telia to become the first 5G airport in the world, leveraging the new technology to enhance airport operations as well as passenger experience. Brussels Airport teamed up with Nokia and operator Citymesh to launch a 5G-ready network.
According to a Nokia white paper, most airports do not have the Wi-Fi networks or the public mobile networks capable of supporting the complex digital demands of these time-sensitive distributed operational environments.
Airport connectivity infrastructures typically combine Wi-Fi and public cellular connectivity into one network environment shared across passenger and operations applications. However, operational challenges, like poor signal strength and traffic congestion, together with the emphasis for greater reliability, autonomy, and the need to power modern bandwidth-intensive applications are centering the focus on private 5G networks.
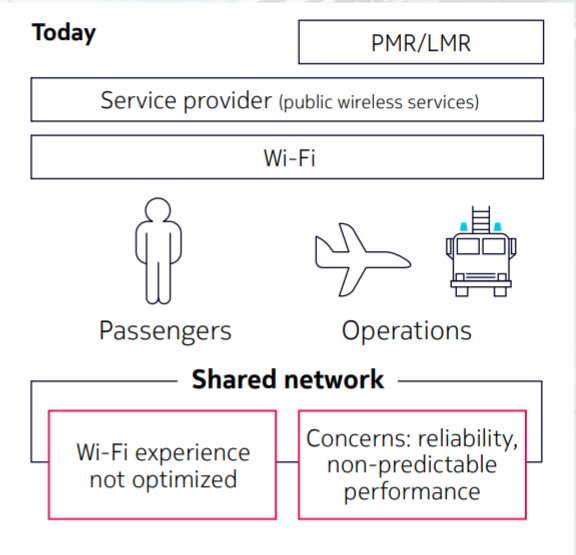
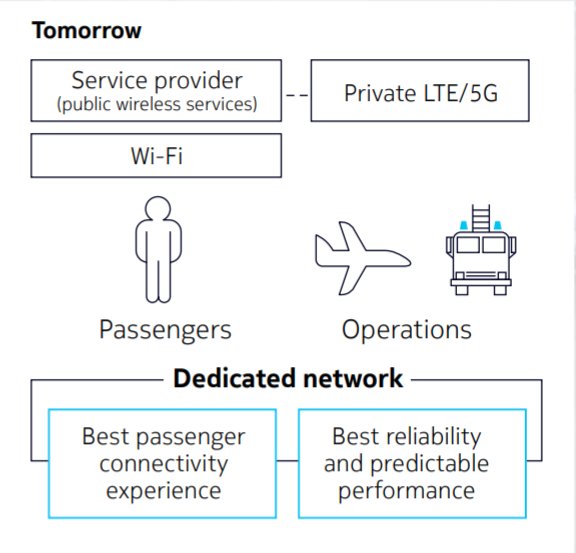
Image source: Nokia
Nokia's proposed wireless strategy for intelligent digital airports does not completely eschew wi-fi and public networks, dedicating these "best-effort networks" exclusively to passenger-side services. All operational services, meanwhile, are handled by “private right to use” networks like 5G.
This dual-pronged strategy not only enhances passenger experience with dedicated capacity but also ties in with some of the strategic business considerations facing digital airports today.
Private 5G networks minimise the dependency on third-party wireless service providers and give airports the opportunity to design the infrastructure that best fits their digital transformation goals. Technology investments can now be made with a more long-term strategic perspective that accounts for the unique budgetary and operational requirements of each location while providing a clear path of evolution to the next generation of technologies.
This approach not only helps manage the total cost of ownership but also enables operators to expand their digitization programs while ensuring robust reliability and security of the wireless infrastructure.
Healthcare - Telemedicine
Healthcare, according to the Ericsson study, is the largest addressable market across the 10 sectors that were analysed. The current COVID-19 pandemic has catalysed this sector, historically one of the slowest to adopt technology, to harness the value of 5G-enabled networks to cope with the sudden surge in patient flow, while observing the guidelines of minimal contact, by optimising the distribution of medical resources.
For instance, a hospital in Wuhan, the epicenter of the global outbreak, leveraged the speed, reliability, and quality of 5G technology to deploy a fleet of robots for patient care and facility management.
In Malaysia, 5G-powered drones with heat-sensing technology have been used for contactless temperature screening of large crowds.
Earlier this year, the West China Second University Hospital and China Telecom launched the world’s first 5G medical private network that would enable the transmission of vast amounts of data and allow doctors to consult with their peers in 27 other locations.
This next-gen network targets five distinct use cases — intra-hospital monitoring, mobile ward rounds and remote consultation, wireless specialist diagnosis, remote surgery and teaching, and emergency response — that are representative of the gamut of 5G-enabled possibilities in the healthcare space.
Today there is little doubt about the fact that 5G wireless networks will play a critical role in unlocking new solutions in preventive, diagnostic, and therapeutic care. And telemedicine is uniquely positioned to benefit from 5G-specific features such as network slicing.
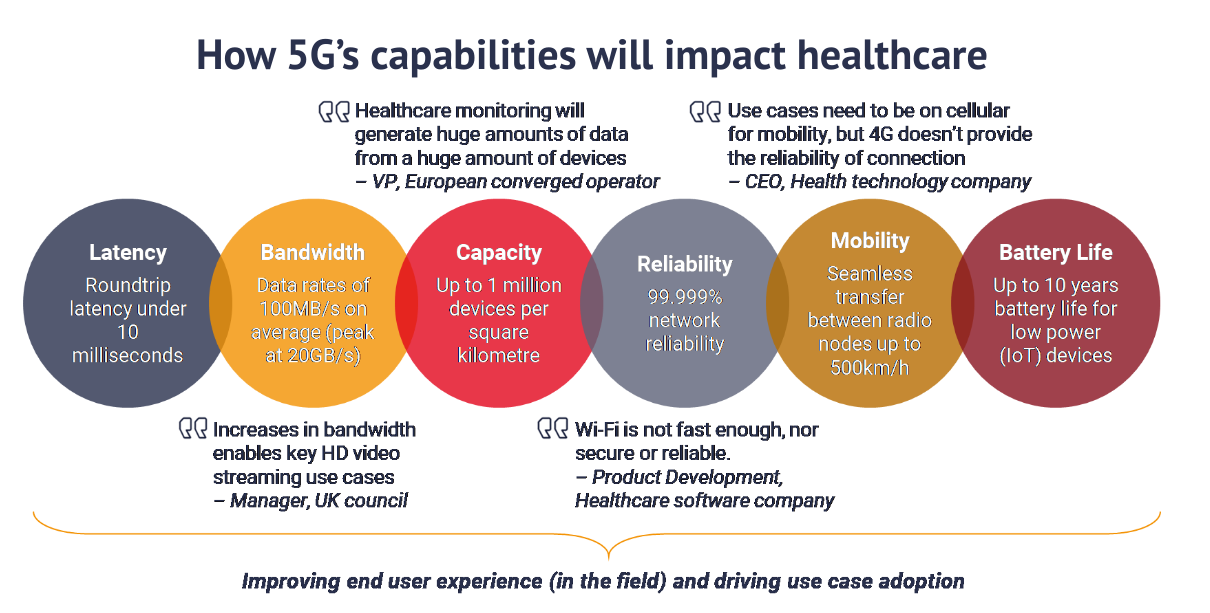
Image source: STL Partners
The coronavirus-5G experiment seems to have piqued the interest of patients in telemedicine with 83% planning to continue with telemedicine even after the current contingencies. Even hospitals are priming up for this potentially new normal with a recent AT&T- HIMSS research revealing that 66% are making progress in digital transformation to advance telehealth.
Another global survey found that 42 percent of healthcare providers had firm plans for 5G deployments. And the telehealth market itself is expected to triple by 2025, fuelled largely by 5G.
Manufacturing - Industry 4.0
The unique benefits of 5G, and their potential for facilitating new use cases and innovations, could unlock $740bn of value in manufacturing by 2030. And 5G, along with Edge Computing and IoT, is expected to be a key enabler of Industry 4, according to a 2020 report from Bloor Research.
In fact, 5G networks will be especially critical to the development of Industry 4.0 as current generation networks may not be able to manage connectivity across 20 billion IoT devices and support the transfer and processing of extremely huge volumes of data.
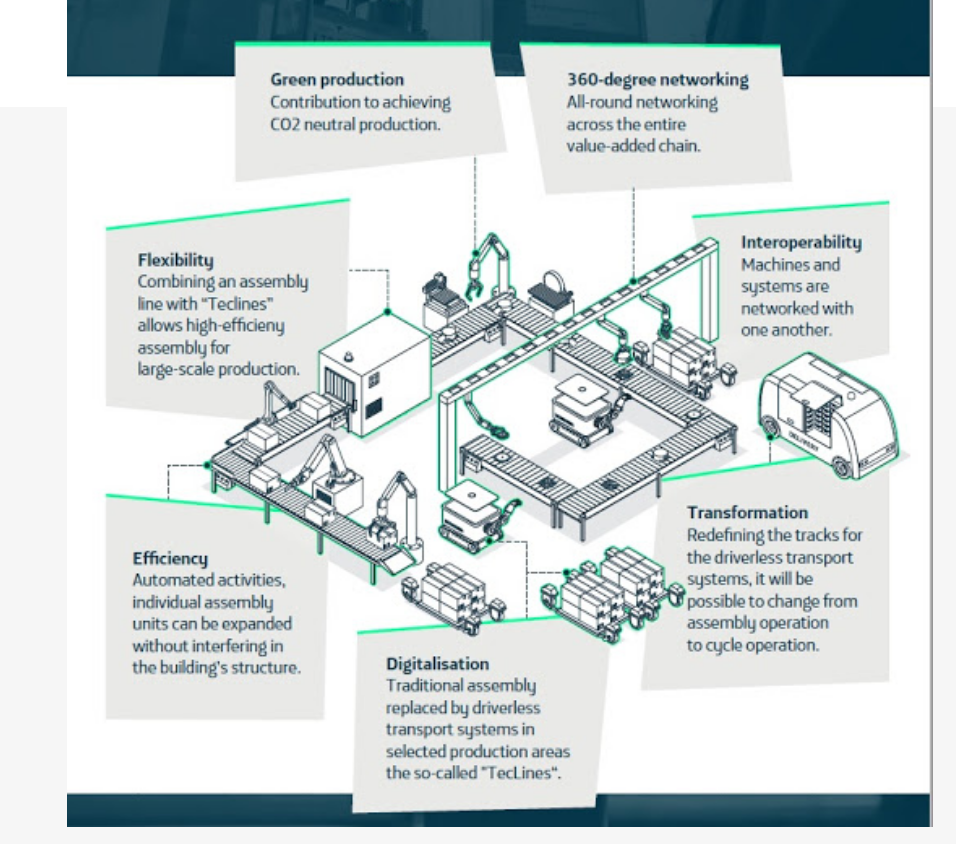
Image source: Telefonica
5G networks will enable businesses to extend Industry 4.0 principles and frameworks beyond the factory floor and across the wider value chain, including supply chain, distribution, warehousing, and customer service.
A unified 5G solution can provide end-to-end connectivity to link together multiple siloed systems, creating new use cases for enhancing efficiencies and costs across the enterprise.
The promise of 5G has prompted a growing number of companies with distributed enterprise environments to opt for private in-house wireless networks over MNOs. The private model offers several significant benefits such as the ability to optimise networks for their unique requirements, the flexibility to reconfigure/upgrade alongside evolving business objectives, and the agency to control and secure all proprietary information.
These are just three use case examples out of a possible 200 plus 5G-led use cases across different sectors. But no matter the sector, the pace of private 5G adoption will be determined by ecosystem partnerships involving multiple stakeholders, including CNOs, communication and industrial technology providers, systems integrators, and Tier 1 manufacturers.
Partnering for 5G growth
Private 5G networks represent a radical shift in the way that businesses consume connectivity technologies.
In January this year, telecom research and analysis company Heavy Reading, supported by Ericsson, Intel, NetNumber, and Qualcomm, launched a report on the dynamics and sentiments driving important private network ecosystem issues based on a survey of telecom operators and enterprise end-users.
Over half the operators in the survey expect private mobile networks to be a major contributor to their enterprise business within five years. And both operators and enterprise users had a favorable view of ecosystem partnerships.
However, there were some minor variations between both groups on the topic of project leadership. Nearly half (48%) of the operators expected to lead private network engagements, with support from other vendors and integrators. Enterprises, on the other hand, placed a high value on multi-party engagement with the largest proportion (27%) indicating a preference for a combination of telco, vendor, and integrator.
That important nuance notwithstanding, productive partnerships are going to be central to the success of private 5G networks.
Our own partnership with Verizon is structured to accelerate customers’ business strategy by combining our unique offerings and competencies.
With Verizon, our enterprise customers can now focus on innovating by tapping into a world-class 5G Ultra Wideband network. With our decades of experience and expertise in professional IT services and high-performance cloud technologies, we enable businesses to align technical network implementations with their strategic business objectives.
Together, we deliver unbeatable IT infrastructure development and world-class management of performance-optimized IT and cloud services across a global operational network.
Learn more about our partnership with Verizon by clicking this link.
Get your FREE copy!
Want to save a PDF version of this post?
Just enter your email below and we'll send you a copy.

