Private and Public Clouds: A Comprehensive Comparison

The advent of cloud computing has revolutionised how businesses manage their data and IT infrastructure. The two primary options for cloud services are private and public clouds, each with their own set of benefits and drawbacks. Below, we provide a comprehensive comparison of the two.
Benefits of Private and Public Clouds
Private clouds are dedicated environments maintained by an organisation or a managed service provider (MSP) for a single client. Key benefits of private clouds include enhanced security, more control over infrastructure, and customisation. Private clouds enable organisations to meet strict compliance requirements, protect sensitive data, and tailor their computing resources to match their unique needs.
Public clouds, on the other hand, are shared environments maintained by a third-party provider for multiple clients. The main advantages of public clouds are cost-effectiveness, scalability, and flexibility. Public clouds offer affordable access to vast computing resources, allowing businesses to easily scale up or down as their needs change, without worrying about upfront investments in hardware or software.
Recommendation: Private or Public Cloud
The choice between private and public cloud depends on the specific needs and priorities of an organisation. For businesses handling sensitive data or subject to strict regulatory compliance, a private cloud is an ideal choice, offering increased security and control. For instance, financial institutions and healthcare organisations often rely on private clouds to maintain the confidentiality and integrity of their data and to ensure compliance with laws such as HIPAA.
Conversely, startups and small to medium-sized businesses (SMBs) with limited IT resources and budget constraints can benefit from the cost-effectiveness and scalability of public clouds. For example, an ecommerce company experiencing rapid growth may find it advantageous to use a public cloud service, such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure, to scale up its infrastructure and meet increased demand quickly.
Agility, Scalability, and Security
- Agility: Public clouds typically offer greater agility than private clouds. With on-demand access to a wide range of services and resources, public clouds enable organisations to adapt quickly to changing business needs. Private clouds, while offering more control, may be less agile due to the additional management and customisation required.
- Scalability: Public clouds excel in scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their computing resources according to demand easily. This is particularly useful for organisations experiencing rapid growth or seasonal fluctuations in demand. Private clouds can be scalable but may require more planning and investment in hardware and software upgrades.
- Security: Private clouds generally offer a higher level of security compared to public clouds. With dedicated infrastructure and more control over the environment, private clouds enable organisations to implement robust security measures tailored to their specific needs. Public clouds, while offering security features, may not be suitable for organisations handling highly sensitive data or subject to strict regulatory compliance. One of the best examples of the risk of the public cloud is the case of Capital One, which was fined $80 million after a data breach on its Amazon Web Services (AWS) cloud servers in 2019 that exposed the personal information of more than 100 million customers. In another shocking case, Dow Jones leaked the data of 2.2 million customers via a misconfigured S3 bucket.
Cost Savings and Pricing Predictability
Private clouds can provide cost savings and predictable pricing for organisations with stable and predictable workloads. By owning and controlling the infrastructure, businesses can optimise resource utilisation, minimise waste, and forecast costs better. However, the upfront investments in hardware and software, as well as the ongoing costs of maintenance and upgrades, can be significant.
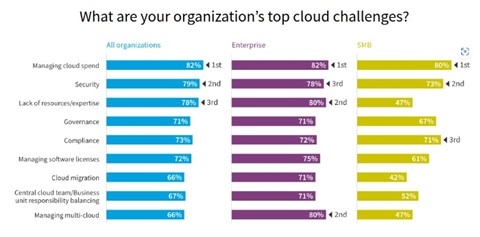
Public clouds offer a pay-as-you-go model, allowing organisations to only pay for the resources they use. This can be more cost effective for businesses with fluctuating workloads or those that do not require extensive customisation or control. However, public clouds can lead to cost spikes in situations where there is a sudden increase in demand for resources or when data transfer costs are high. In addition, pricing predictability is poor in the public cloud. A wrong configuration can easily lead to massive billing surprises. In fact, managing cloud spend is the top challenge for organisations, according to a recent survey by Flexera.
Addressing the Drawbacks of Private Cloud
One major drawback of private cloud deployment is the inherent cost required to procure, configure, maintain, and upgrade hardware and software. Further, training expenses can have a significant impact on the bottom line. To mitigate these challenges, organisations should outsource their private cloud management to a managed cloud provider.
Managed cloud providers offer a range of services, including infrastructure management, security, and compliance, as well as application and data management. By outsourcing these tasks, organisations can reap the benefits of a private cloud while avoiding the complexities and costs associated with managing it in-house.
The Bottom Line
Private and public clouds each offer a unique set of benefits and drawbacks, making a choice between them dependent on an organisation's specific needs and priorities. Sovereign clouds are emerging as a viable solution for addressing data sovereignty and compliance concerns. In terms of agility, scalability, and security, public clouds generally offer greater agility and scalability, while private clouds provide more robust security.
Organisations seeking the benefits of a private cloud without the associated costs and management challenges can turn to zsah's managed cloud services. Ultimately, the decision to adopt a private, public, or hybrid cloud model should be based on a thorough assessment of the organisation's requirements, risk tolerance, and long-term objectives.
eBook - Guide to Managed Cloud Services for Saas Providers
All the knowhow to help you implement a successful managed Cloud Strategy.